In the dynamic realm of online advertising, understanding the nuances of metrics like Cost Per Mille (CPM) in Google Ads is paramount for advertisers and digital marketers alike. As businesses navigate the expansive landscape of Google Ads, delving into topics such as Average CPM, Ad Campaigns, and the intricacies of Cost Per Mille becomes crucial for optimizing ad spend and achieving marketing success.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll unravel the layers of a CPM campaign, exploring the strategies, benefits, and practical tips to elevate your digital marketing efforts. Whether you’re a seasoned advertiser or just stepping into the world of online ads, join us on this journey to decode the intricacies of Cost Per Mille in Google Ads and unlock the potential for higher visibility, engagement, and return on investment.
This article is a segment of a more extensive piece about Google Ads Metrics.
What is CPM?
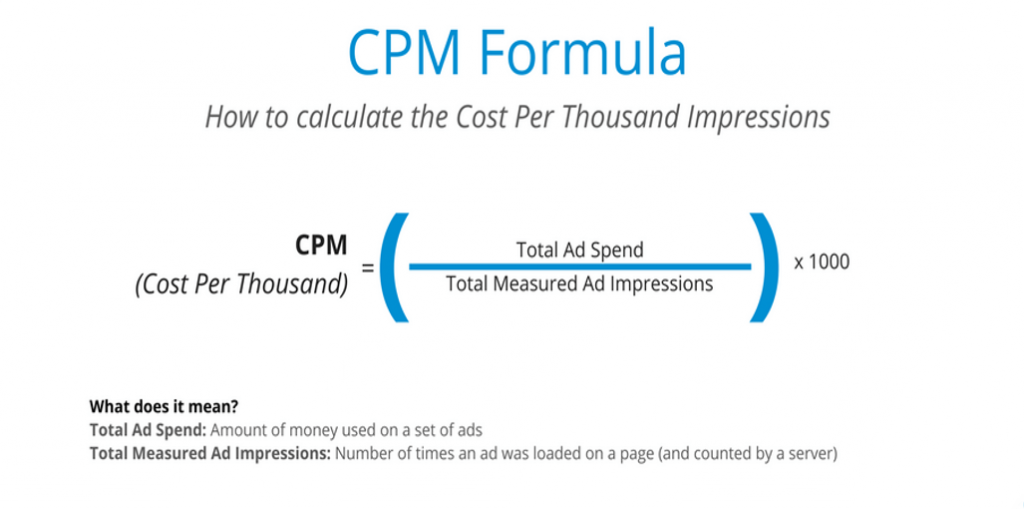
Cost Per Mille, commonly known as CPM, is the cost an advertiser pays per one thousand impressions of their ad. In online advertising, an impression occurs each time an ad is viewed, irrespective of whether the viewer interacts with the ad. CPM serves as a fundamental metric, providing insights into the efficiency and reach of an advertising campaign.
Understanding CPM is pivotal for advertisers aiming to optimize their ad spend and enhance the performance of their campaigns. It forms the backbone of the pricing model in online advertising, allowing adversaries to gauge the cost associated with reaching a thousand impressions, a critical factor in assessing the overall effectiveness of an ad strategy.
As advertisers delve into the intricacies of CPM, various elements come into play, including the type of ad campaign, the target audience, and the platforms chosen for ad placements. Additionally, CPM is closely tied to the concept of Average CPM, which provides a benchmark for evaluating the competitiveness of advertising costs within a specific industry or niche.
In essence, CPM is a foundational metric that, when understood and leveraged effectively, empowers advertisers to make informed decisions, maximize visibility, and achieve optimal results in their digital marketing endeavors. In the subsequent sections, we will explore the diverse facets of CPM, ranging from its role in different ad formats to strategies for achieving a good CPM and the significance of CPM in the broader landscape of online advertising.
What is CPM Used For?

Cost Per Mille (CPM) serves as a critical metric in online advertising, playing a pivotal role in assessing advertising campaigns’ efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and reach. Here are several key purposes for which CPM is widely used:
Cost Measurement
CPM is primarily employed as a pricing model, allowing advertisers to determine the cost of a thousand ad impressions. This provides a clear and standardized way to measure the expenses incurred for the potential exposure of the ad to a specific audience.
Benchmarking and Comparison
Advertisers use CPM to benchmark their advertising costs against industry averages and competitors. Average CPM serves as a comparative tool, helping businesses evaluate the competitiveness of their advertising expenditures within a particular niche or sector.
Campaign Optimization
Advertisers can optimize their ad campaigns by analyzing CPM data to achieve better results. This includes refining targeting parameters, selecting optimal ad formats, and choosing platforms that offer competitive CPM rates.
Budget Allocation
CPM aids advertisers in allocating their advertising budgets effectively. Understanding the cost per thousand impressions allows businesses to make informed decisions about distributing their budget across various campaigns and channels.
Performance Evaluation
CPM is instrumental in evaluating the overall performance of an advertising campaign. Advertisers can assess the cost-effectiveness of their strategies, identify areas for improvement, and refine their approach to maximize the impact of their ads.
Ad Format Selection
Different ad formats come with varying CPM rates. Advertisers use CPM data to choose the most suitable ad format for their goals, whether display text ads, banner ads, video ads, or other formats, based on their budget and target audience.
Platform Comparison
CPM allows advertisers to compare advertising costs on different platforms, such as the Google Display Network ads or social media channels. This comparison helps in strategic decision-making regarding where to allocate resources for maximum visibility and engagement.
In essence, CPM is a versatile tool that empowers advertisers to make data-driven decisions, optimize their campaigns, and achieve the best possible return on investment in the competitive landscape of online advertising. The subsequent sections will delve deeper into specific aspects of CPM, providing insights into strategies for achieving a good CPM< factors influencing CPM rates, and the role of CPM in different ad campaigns.
CPM in Google Ads: Maximizing Visibility and Efficiency

Cost Per Mille (CPM) is a crucial metric within the expansive realm of Google Ads, the widely utilized platform for online advertising. Google Ads offers advertisers a versatile ecosystem to showcase their products or services across the Google Display Network (GDN), Google Search Ads, and other affiliated platforms. Understanding and effectively leveraging CPM in Google Ads is essential for advertisers looking to optimize their ad spend and achieve optimal results. Let’s explore the significance of CPM within the context of Google Ads.
Google Display Network (GDN)
CPM plays a significant role in ad placements across the Google Display Network. Advertisers bidding on a CPM basis pay for every one thousand impressions their ads receive. This model is particularly beneficial for campaigns focused on brand awareness, as it ensures a predetermined cost for a specified number of views, irrespective of click-through rates.
Ad Format Selection
Google Ads supports various ad formats, each with its own CPM rates. Advertisers can choose from display text, banner, video, and more. Understanding the CPM associated with each format is crucial for selecting the most suitable option based on campaign goals, target audience, and budget constraints.
Targeting and Ad Placement
CPM in Google Ads is closely tied to targeting parameters and ad placement strategies. Advertisers can optimize CPM by refining their audience targeting to reach the most relevant users and selecting strategic ad placements that align with their campaign objectives.
Average CPM Benchmarks
Google Ads provides valuable insights into average CPM benchmarks within specific industries or niches. Advertisers can use this data to compare their CPM rates against industry standards, helping them gauge the competitiveness of their advertising costs and make informed adjustments to their strategies.
As of November 2023, advertisers stepping into Google Ads are met with an average CPM of $2.80. This provides a baseline for comparison, allowing advertisers to benchmark their costs against industry standards. Regularly assessing and comparing CPM rates aids in making informed decisions and optimizing CPM campaigns.
Google AdSense CPM
CPM is a critical factor in revenue generation for publishers utilizing Google AdSense to display ads on their websites. Adsense CPM rates vary based on website niche, ad format, and audience demographics. Advertisers and publishers alike benefit from understanding and optimizing CPM for mutual success.
CPM Advertising Strategies
Advertisers on Google Ads can employ various strategies to optimize CPM. This includes refining ad creatives, implementing effective ad targeting, and strategically adjusting bids based on performance data. Automated scripts and tools within the Google Ads platform further maximize CPM efficiency.
CPM in Google Ads is a linchpin for advertisers seeking to balance costs, visibility, and audience reach. Advertisers navigating the Google Ads landscape should harness the power of Cost Per Mille to make data-driven decisions, refine their campaigns, and ultimately achieve the best possible outcomes in the ever-evolving world of online advertising.
Achieving Precision in Advertising: Target CPM Strategies with Examples

In Google Ads, Target CPM (Cost Per Mille) emerges as a strategic beacon for advertisers aiming to achieve precision and efficiency in their campaigns. This approach allows advertisers to set specific cost expectations for one thousand impressions, providing a structured framework for budget management, visibility optimization, and overall campaign success. Let’s explore Target CPM strategies and explore real-world examples showcasing its efficacy.
Defining Target CPM
Target CPM is the predetermined cost per one thousand impressions that advertisers set as a goal for their campaigns. This strategic approach empowers advertisers to control costs, ensuring campaign expenses align with predefined objectives.
Example 1: Strategic Bid Adjustments
Scenario: A leading tech company aims to maximize visibility for its latest innovation within a specified budget. By setting a Target CPM, the company strategically adjusts bids for specific audience segments within the tech community, ensuring efficient use of the budget while achieving the desired impressions for their cutting-edge product.
Precision in Budget Management
Target CPM provides advertisers with precision in budget management. Advertisers can allocate budgets more effectively, knowing they are working towards achieving a specific cost per impression that aligns with their overall campaign objectives.
Example 2: Budget Allocations for Brand Awareness
Scenario: A tech startup in the highly competitive industry seeks to enhance brand awareness without exceeding a specific budget. Implementing Target CPM, the startup strategically allocates budget resources to maximize visibility and brand exposure within the tech landscape. This precise budget management allows the startup to create a significant impact, ensuring widespread recognition while adhering to cost expectations in the tech-savvy market.
Strategic Bid Adjustments
Advertisers can make strategic bid adjustments based on the defined Target CPM. This ensures that bids are aligned with the desired cost for reaching a thousand impressions, allowing advertisers to optimize their campaigns for specific audiences and placements.
Example 3: Ad Creative Optimization for Lower CPM
Scenario: A tech solutions provider with a Target CPM goal employs creative optimization techniques. Crafting engaging ad content that highlights technological innovations, the company enhances user engagement and achieves a lower CPM due to improved ad quality, ensuring their message reaches a tech-savvy audience effectively.
Maximizing Visibility with Target CPM
Target CPM is particularly valuable for campaigns that maximize visibility and brand exposure. Advertisers can fine-tune their targeting parameters to reach the most relevant audiences while adhering to the predetermined cost per impression.
Example 4: Targeting Niche Audiences for Efficacy
Scenario: A tech gadget brand targets a niche audience interested in cutting-edge innovations. Setting a Target CPM, the brand optimizes its campaigns to reach tech enthusiasts, ensuring maximum visibility among individuals who align with their brand values and have a heightened interest in tech products.
Flexibility for Different Ad Formats
Google Ads supports various CPM ads, and target CPM allows advertisers to customize their approach for different formats. This flexibility lets advertisers choose the most cost-effective strategies based on campaign goals and audience preferences.
Example 5: Tailoring Approach for Video Ads
Scenario: A tech device manufacturer utilizes Target CPM for video ad campaigns. Acknowledging the higher CPM associated with video ads in the tech sector, the manufacturer strategically adjusts bids to achieve the desired impressions cost while maximizing the impact of their video content, showcasing the latest tech innovations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the digital advertising landscape within Google Ads is intricately woven with diverse metrics and strategies, each playing a unique role in shaping the success of campaigns. From the granular insights derived from Ad Impressions and CPM Campaigns to the strategic considerations of Ad Networks and Google AdWords, advertisers navigate a dynamic environment where precision and adaptability are paramount. Understanding the nuances of the CPM Model and the intricacies of metrics such as Click Through Rate (CTR) and Average RPM empowers advertisers to make informed decisions, optimize ad views, and achieve the delicate balance between cost, visibility, and engagement.
As advertisers strive to maximize the impact of each click and navigate the complexities of the digital marketplace, factors such as targeted audience precision, strategic bid adjustments, and the continuous monitoring of Other Metrics become instrumental. The journey of online advertising extends beyond the singular focus on CPM; it encompasses creating engaging and relevant ad content, strategic targeting, and a nuanced approach to budget management.

A PPC specialist who started with organic social media. For several years, the core of his activities are:- Google Ads, Microsoft Ads, Meta Ads, TikTok Ads, Twitter Ads, Linkedin Ads. He has led campaigns with a global reach, e.g. for FootballTeam, G2A, ETOTO, as well as many smaller campaigns in the sports, construction and financial industries. Has full focus on ROAS. Privately, a fan of football, history of wars and Star Wars.