The volatility of crypto markets allows traders to speculate on the price movements to find the best positive trading opportunities. The first iteration and the most popular that traders have is spot trading.
It is one of the most known investment trading methods that offers ways to invest and trade financial assets with ease. And through this article, you will learn how it works, the difference between spot markets and other sorts of trading methods, and the benefits and risks of utilizing the spot trading method.
What is Spot Trading
Spot trading is when a trader tries to make a trading profit in the market by purchasing an asset at a certain market price, hoping to sell it at the spot market for a better price later. Sometimes spot traders can also short the market by selling financial assets and repurchasing much more when the price decreases.
A key element to keep in mind about spot trading is the spot price (the current market price). Spot prices change in real time, and you can set up different methods to take advantage of price fluctuations, which we will discuss later in detail. But the most used of all in-exchange services is a market order, where you can purchase or sell assets immediately at the available spot price. However, there isn’t a guarantee that the market price won’t change during the order, and there might not be enough volume to satisfy your order at the price you wanted.
Spot markets exist for all types of assets. The asset will be on for immediate delivery or within T+2 days (trade date plus two business days). In traditional markets, equities and shares require a transfer of physical certificates. For foreign exchange market, people previously transferred currencies via cash, deposit, or wire.
Now with a digitized system, these deliveries will occur immediately and are crucial for crypto spot trading, which operates at every hour, every day, and usually allows you to make instant trades. The time might differ for Peer-to-peer and over-the-counter.
How Anyone Can Profit from Spot Trading
As we stated before, one buys assets on trade spot markets to sell them for more later on. This method of investing lets you hold your tokens for many years.
Over crypto markets, traders use spot markets using a dollar-cost-averaging strategy into the cryptocurrency they desire and wait for the next bull market to make profits. Patient traders generally receive good profits since crypto coins tend to go up over time. Although, it’s important to remember that the profits will get real after you sell your cryptocurrency for fiat currency (traditional money) or for a stablecoin of choice.
Benefits of Spot Trading
There are many benefits to implementing spot trading to acquire crypto assets:
- It is less risky compared to margin-based crypto trading. You won’t be liquidated by price fluctuations.
- You can easily measure your risk or reward when you trade in the spot market.
- Since transactions happen in a transparent process based on demand and supply, spot trading gives you the prices of cryptocurrencies more precisely.
- It allows you to use crypto assets for other services, like making online payments or staking.
- It allows you to trade over a wide variety of cryptocurrencies as opposed to other types of trading over the financial market, with fewer currency pairs.
Risks of Spot Trading
Not everything can be good news, as spot trading also have its fair share of risks:
- Chance of dry liquidity: Liquidity can dry up over time in spot markets. Especially during bear markets, as smaller altcoins tend to lose most of their liquidity. This will result in traders struggling to find a place to sell their digital assets for fiat at a good market price. Then, you will be forced to hold on to your investments or sell them at a lower price.
- Commodities: Another risk that will present itself is when you determine to trade commodities on the spot market. For example, if you spot purchase crude oil, you need to have it delivered physically.
- Limited Potential: As spot trading does not allow for margin, potential gains in the spot market are lesser than margin trading or Contracts-for-difference (CFD).
- Unregulated: This can be mitigated by spot trading on reputable exchange services (like Binance) and markets. The crypto industry is a “no man’s land” when we talk about regulation, and if anything happens when purchasing any crypto asset, you are on your own unless the exchange service provides a solution for your issue.
Spot Market: Different Types Available
Luckily, spot trading isn’t limited to one single place. Usually, most individuals will do spot trading on exchanges. However, you can also trade directly with others without a third party. Each spot trading markets have its own differences.
Over the Counter (OTC)
Also known as off-exchange trading, financial assets and securities are traded directly between dealers, brokers, and traders.
It uses multiple communication methods to organize trades, including instant messaging and phones. They are private and less regulated than the normal exchange landscape. They allow traders to sell and buy larger amounts of crypto without moving the market price too much.
Over-the-counter trades have some benefits from not using an order book. Large OTC trades often get better prices than the usual method. When trading an asset with low liquidity, a large order can cause some slippage, and the exchange can’t totally fill your order at a price wanted. This means that you have to pay a higher price to complete the transaction.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P)
Peer-to-peer trading allows people to trade cryptocurrencies among themselves. It can be carried out without the involvement of third parties, similar to what happens with OTC.
It gives you more control over the trading activities like choosing buyers, and sellers, settlement time, pricing, and payment methods. Most of the P2P platforms require creating bids and offers using these preferences to make trades smoother.
P2P trading can suffer, though, from low liquidity and slow settlement time. Also, it’s a risky environment as there aren’t third parties facilitating trades via escrow services between traders.
Centralized Exchange
A centralized exchange manages the trading of assets like commodities, cryptocurrencies, and forex. The exchange service acts as a custodian of the traded assets and as an intermediary between market participants. Usually, to use an exchange service, you have to load up your account with the crypto you want to trade or with fiat currency.
A centralized exchange needs to make sure transactions happen smoothly. It has to regulate compliance, fair pricing, KYC (know your customer), customer protection, and security. It is considered safer than other trading markets. In return, they profit by charging fees on listings, transactions, and other trading activities.
As long they have enough customers and trading volume over their platform, exchanges will profit even in bull and bear markets.
Decentralized Exchange
A DEX (Decentralized Exchange) offers many of the same basic services as a centralized exchange does. But it matches buying and selling orders through the use of blockchain technology. In most cases, you don’t need to create an account to trade with one another or transfer assets onto the DEX.
The trades occur directly between digital wallets through smart contracts. These are self-executing pieces of code located on the blockchain. It comes with more privacy and freedom, but the lack of KYC and customer support can be an issue if you have any problems during the transaction.
Some DEX uses an order book model, like Binance DEX. Another model is the Automated Market Maker (AMM), used in exchange services like PancakeSwap and Uniswap.
This AMM model also uses smart contracts, but it implements a different model to set up prices. Traders use funds in a liquidity pool to swap their tokens, and providers charge transaction fees for anyone who uses the liquidity pool.
Differences With The Futures Market
Futures trading works differently to spot markets because you don’t own the underlying asset. However, futures trading merely represents the value of such assets.
This market has futures contracts that will be paid for at a future date. The traders agree to trade a certain amount of assets for a specified price in the future. When a futures contract reaches its expiration date, the buyer and seller agree to resolve the trade-in cash rather than exercising the contract.
Key Concepts of Margin Trading

Margin traders use borrowed funds to pay for a trade. It allows the trader to open a position without having to pay all from their own pocket. To further explain this concept, there are several key elements to understand first.
Leverage
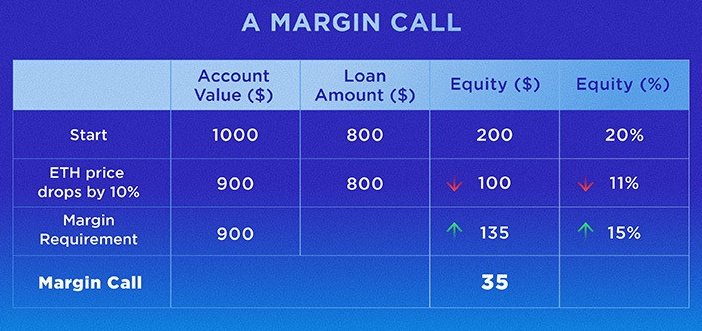
It refers to the use of borrowed funds to pay for a trade. The amount of leverage that can be used will vary across different trading and exchange platforms. And the value of the account balance, based on the current price in the market, minus the borrowed amount, is known as equity.
Margin
Due to price fluctuations, the equity will also suffer from this. When the equity level drops below a certain point (this threshold is known as the Margin Requirement, previously set by the exchange platform), the trader will get a Margin Call.
When you reach the Margin Call, you have to sell some or all of their position and/or compensate, if required, with your own funds into the account in order to bring the equity value back up to the margin level.
Liquidation and Collateral
If a trader fails to meet the Margin Call, the platform can sell the assets that the trader has in its account (referred to as Liquidation) and use the proceeds to pay down the loan.
These assets that the platform took from the trader to pay for the loan are known as Collateral.
Main Differences Between Spot Trading and Margin Trading
While spot traders can buy assets with their own money, margin traders will borrow capital to purchase crypto or stocks. This allows them to buy larger quantities, with a bigger potential than a spot trader could achieve.
However, this will require you to meet margin requirements to avoid a Margin Call. As the costs of a margin loan can pile up, most margin traders do their business in a short time frame. It is riskier, as a losing margin trade can cost you even more than your initial investment.
Closing Thoughts
Spot trading is one of the most common ways for people to trade, especially for beginners and everyone that want to introduce in the market with cryptocurrencies.
Though it is really straightforward, it’s always nice to have more knowledge about the topic and spot when you can take advantage of it, when you are at a disadvantage, and plan any strategy to profit. And with this guide, you will be able to do all of this!

SEO enthusiast and digital marketing strategist. My expertise lies in optimizing websites for organic traffic growth and search engine visibility. I carry out, among others, SEO tests, keyword research and analytical activities using Google Analytics. Privately, he is a lover of mountains and bicycle trips.

