According to Ahrefs’ study, almost 91% of web pages are invisible to search engines.
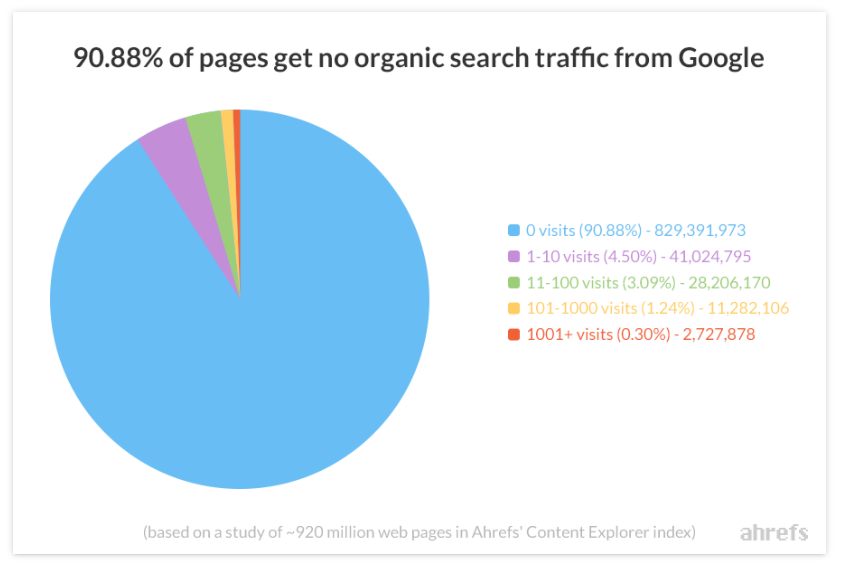
It shows how important it is to have your website’s SEO on point.
With our step-by-step DIY SEO audit guide, you will know:
- When you need an SEO audit;
- How to do it yourself;
- What tools are useful in doing an SEO audit;
- How much it costs to order an audit.
Read later: Is SEO Worth It for Small Business? We believe so
What Is an SEO Audit and Why Is It Important?
A comparison of an SEO audit to a health check is something that all SEO experts love.
The definition from Three Deep Marketing says:
“An SEO audit is a process of analyzing how well your web presence relates to best practices – it is the first step to creating an implementation plan that will have measurable results.”
Here are crucial factors regarding an SEO audit:
- Technical SEO – Page speed, accessibility, indexing;
- Website structure and site architecture;
- On-page SEO issues – 404 errors, thin content, internal linking, broken links;
- Off-site problems – Backlink analysis, lost backlinks;
- User experience issues;
- Content gaps and keyword opportunities;
- Competitive marketplace insights.
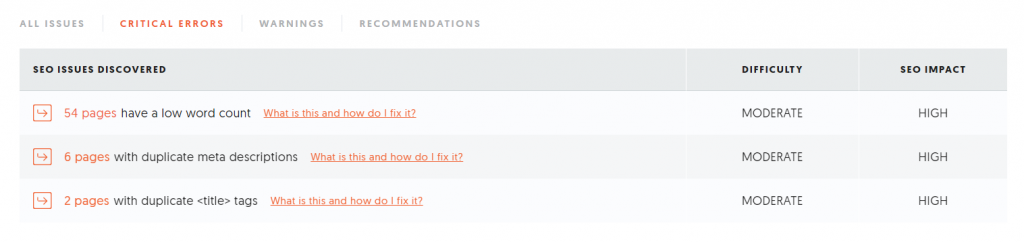
Even though it may sound complicated, sometimes fixing just the basics can bring extraordinary results. This is an example of a case study of one of our clients.
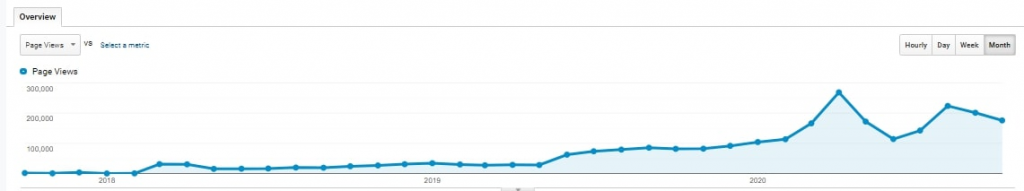
When we started working together, all pages had the same page titles and meta descriptions. We had to fix it first.
Then, we added lots of unique content. Many pages had a low word count. We also filled category pages with good, converting descriptions.
The SEO strategy we have designed provided our client with 250,000 unique visitors monthly in less than two years.
Performing an audit is a win-win situation.
If an ordered audit shows that something is wrong with your website, you’ll be aware of it, and you will be able to start looking for a solution. However, if everything is fine, you’re golden, and you can only improve from then on.
Most prominent SEO figures like Rand Fishkin, Brian Dean, and Neil Patel say that SEO never ends.
With hundreds of changes in the Google algorithm each year, there is always something to work on. Solutions that worked for you greatly in January 2021 might be outdated five months later.
Step by Step SEO Audit [checklist]
When your PC is not doing well, you’re checking it piece by piece – CPU, GPU, RAM, HDD, motherboard, etc. until you find the one element which drags the whole unit down.
The same goes for an SEO audit.
Once you notice something is wrong, you need to check your website step by step.
We can divide an SEO audit into two major parts:
- On-site Audit – Here, you have to check everything within your domain, from indexability all the way to schema markups on each site.
- Off-site Audit – In this part, you will mostly be checking and fixing your link profile, managing your website’s authority, perception, and brand awareness outside of it.
There is a debate about which part – on-site or off-site – is more important. We’d side with those who start with On-Site optimization. Let’s be honest; even the most valuable backlinks will not help if you have garbage content. Not to mention that low-quality content will not give you high-quality links.
Here’s a nice, newbie-friendly guide on what to look for during an SEO audit.
Step 1. Website Visibility Check
It should be your starting point. There is no Search Engine Optimization if search engines don’t see your website at all.
You should have your Google Search Console up and running by now. There, you have an option to check the status of any given URL within your domain.
The tool will show you all indexation issues:
- URL is not indexed;
- URL is indexed but not uploaded in a website’s sitemap;
- URL is indexed, but it has issues;
- URL is indexed and it has no errors.
Alternatively, you can use the command “site:” in Google Search Box.
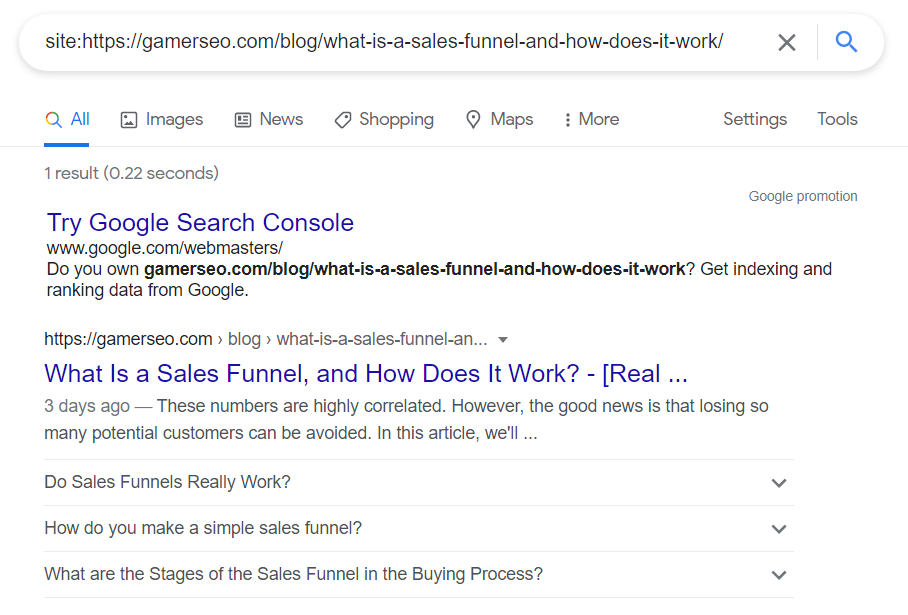
If Google doesn’t see your URL because it’s not indexed or blocked, it should return a result like this:
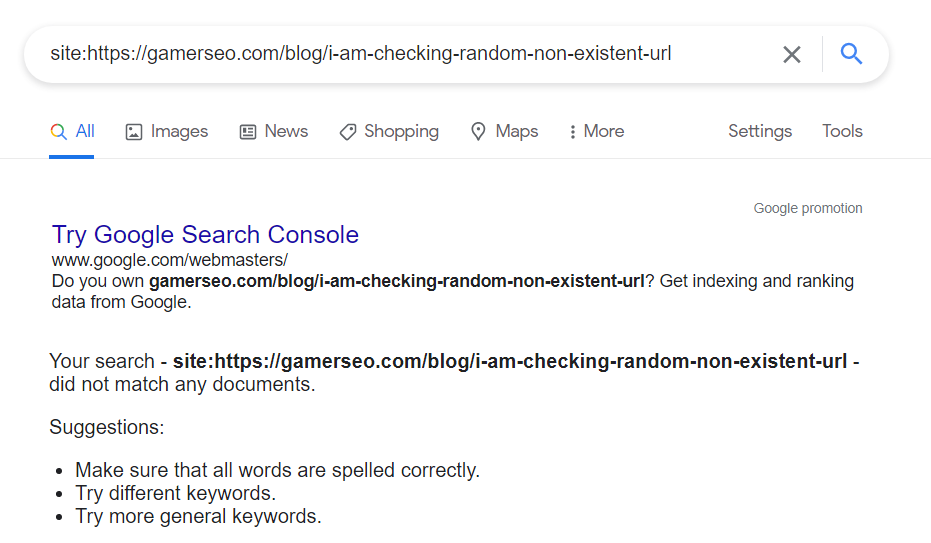
Another mistake you might have made is messing up your robots.txt file. For example, you might click something you shouldn’t click in an SEO plugin like RankMath or Yoast SEO, which changes the “index” attribute.
Step 2. Make Sure There Is Only One Version of Your Site Available
If we made a mistake, we’d have at least four versions of our website.
- http://gamerseo.com
- https://gamerseo.com
- http://www.gamerseo.com
- https://www.gamerseo.com.
For Google, these are four different websites.
Four separate websites with the same content. Any search engine will see that as duplicate content.
If Google has indexed it already, you need to 301 redirect them to one address. We’ll talk about 301 redirects later on.
| Pro tip: We recommend you have the HTTPS version of your website. Having an SSL certificate on your website is a ranking factor. |
Step 3. Meta Tags
Every page on your site has its own title, H1 tag, and meta description. It’s like a first name, last name, and a bio. You’ve got to type in these data separately for each page.
If you fail to do so, it will be set to default, which, in most cases, results in duplicating the data from the home page.
And Google doesn’t like duplicating.
| Protip: These are only guidelines for Google, as it can determine the metadata on its own. However, it is better to guide Google than to let it choose for you. |
It is not the only benefit of having your metadata fixed. Remember that the title tag and meta description are important in terms of organic Click-Through Rate. If you want to have an edge in the search engine result page battle, fix them asap. Also, make sure you have only one title tag, H1 tag, and meta description per page.
Step 4. Check Your Organic Search Traffic
You must have asked yourself a question: “Why is no one coming to my store?” or “Why don’t I make sales?” It is one of these SEO issues that trigger people to check if everything with their SEO is in order.
If you’ve asked yourself these questions, it means you do have a problem.
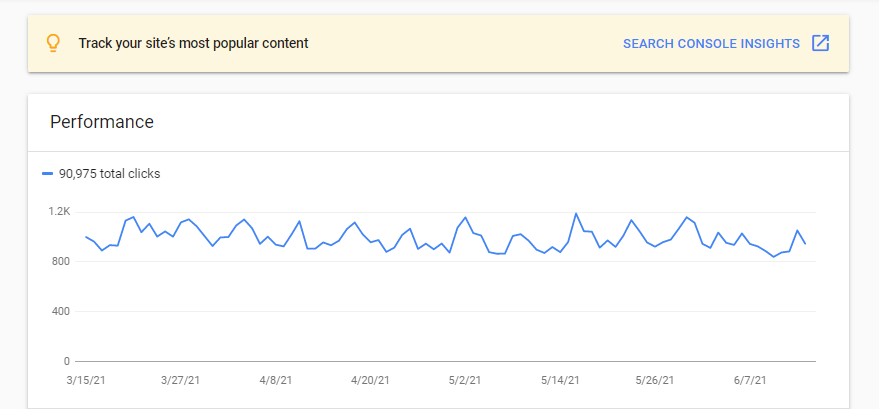
Google Search Console and Google Analytics should be the first tools to show you that there is an issue. You can also use free tools as well as paid tools to check it. However, the conclusion is always the same – you need more traffic no matter how good your website is.
For now, let’s focus on the issue of having (or not having) any traffic.
Does your Google Search Console look like this?
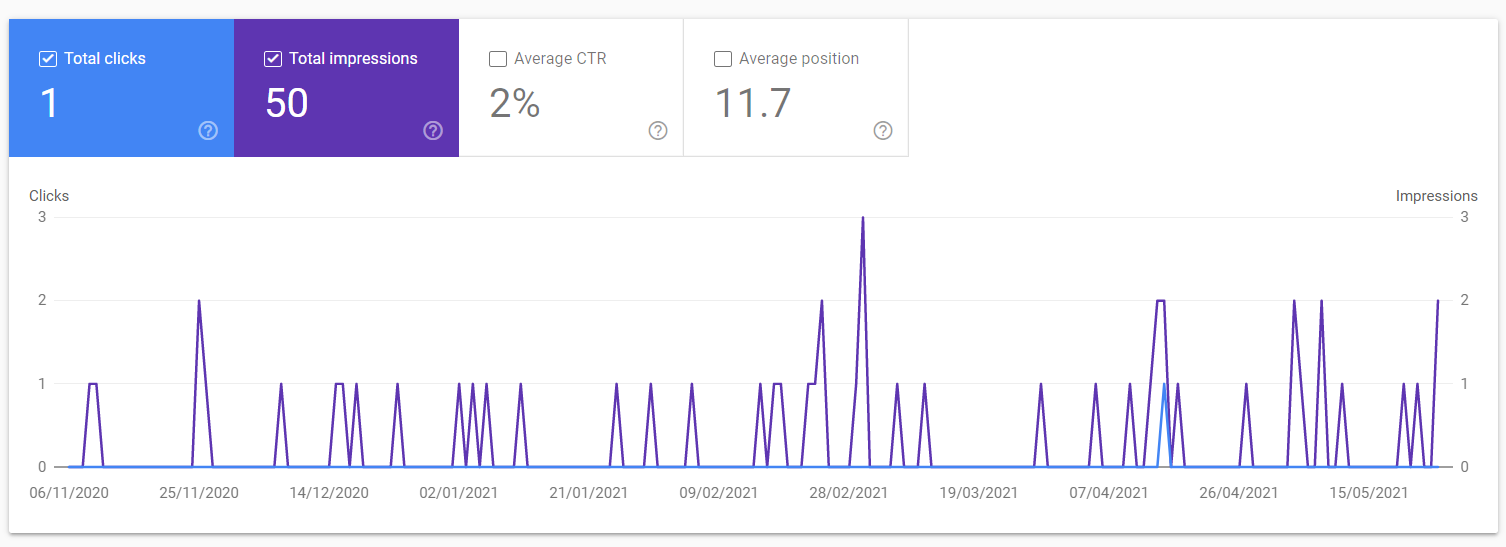
Maybe your Google Analytics traffic chart looks like this?
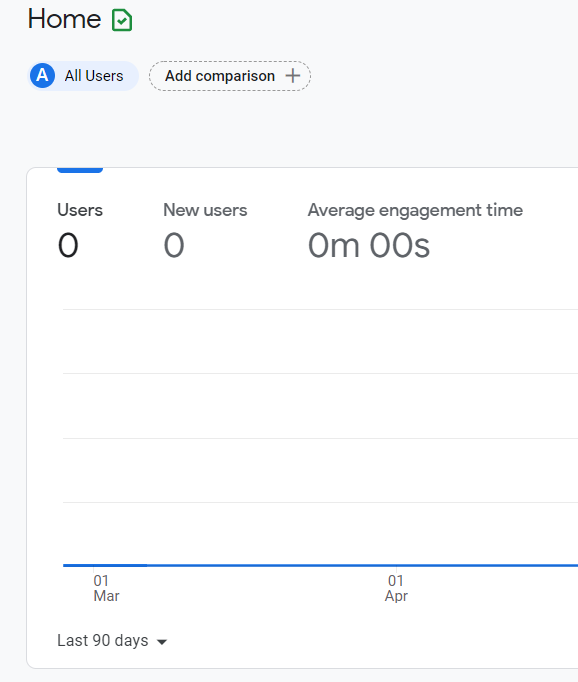
If it does, you need help.
Step 5. Optimize Content on Your Site
Content optimization revolves around two things:
- Search Engine Optimization – Make sure you have the search term in H1, title tag, meta description, and first 150 words of your content. You should also use LSI keywords (related ones) with correct density.
- User Utility Optimization – Correct keyword placement is important but not as crucial as overall content quality and utility. The Internet is crowded with people searching for answers, and your sites need to focus on answering their needs.
You want to have high-quality content for several reasons.
- High-quality content pages give you higher chances to acquire a backlink;
- High-quality content has better options to end up high in search rankings.
We will go over the most common content issues.
Duplicate Content
Duplicate title tags and meta descriptions are a problem, as well as duplicate on-site content.
Technically, there is no Google penalty for duplicate content. If Google finds two, as they call it, “appreciably similar” pieces of content on the Internet, they’ll have trouble determining which one is the original.
The most common mistakes here:
- Pagination Pages – Each subsequent page will copy the metadata from the previous page.
- Missing title tags and meta descriptions – In such a case, Google will automatically select the meta data, taking it from the home page, most likely. There is a risk it will be duplicated.
- Copying the product description – Are you selling Secretlab gaming chairs? You may have taken the description from the producer’s website, just like any reseller out there. Guess what? You all have duplicate content now.
Thin Content
In simple words, thin content is the type of content with little to no value for the user.
In new SEO guidelines, there is a text to HTML ratio. This is the ratio of visible text to HTML elements invisible for the user.
According to SiteGuru, an ideal text to HTML ratio goes from 25% to 70%.
Landing Pages
Landing pages on your site are the place where you want your visitors to land. These pages are supposed to give your business sales.
We suggest you use tools like SurferSEO to optimize the content and make sure the its structure is on point.
Landing pages have a different purpose than blog posts. They need to convert – generate leads, make users leave their email address, or buy your product. For that, you may need to hire a good copywriter.
Articles, Blog Posts, and Other
Finally, once you have all the above fixed, you can focus on your posts.
Blog posts – articles and guides – are essential for your sales funnel. They gather organic search traffic and build your website’s authority.
Read also: Why Have a Company Blog: 7 Fact-Based Reasons
How much does a blog cost? It depends on its size, the industry, the quality of content, and many other factors. However, in general, the ROI on a blog is way higher than any PPC campaign.
Structured Data
This is a kind of decoration in comparison to elements we spoke about before.
However, it can help your organic traffic. Adding some flair to your content makes it stand out on the search engine results page. This may give you an additional click or two.
Structured data is an element of metadata placed within the website code that tells Google what is what. There are a lot of types of schema markup, and you can find them on schema.org.
Using them may cause your search results to look like this.
Keyword Optimization
You don’t want to upload random content and hope for it to work. You need to focus on money keywords (if your goal is sales) that will attract your target audience.
Each landing page has to be optimized for particular search terms.
Step 6. Optimize Your Site for Mobiles
Mobile-First Index was introduced back in 2019. It means that each page is indexed for mobile devices first.
Therefore, you want to make your website mobile-friendly for the sake of both mobile and desktop search results.
First, you want to use a Google Mobile-Friendly test to check whether your website is mobile-friendly.
Second, you need to fix all the issues. The most common ones are:
- Different content for mobile and desktop;
- Small, unreadable font;
- Interactive elements too close to each other;
- Page speed issues;
- Lack of responsiveness;
- Large page size.
Third, you have to stick to the best practices regarding mobile-friendliness on a daily basis.
- Keep your website light.
- Use a large, readable font.
- Always think of mobile users when creating the next piece of content.
- Take a look at your website from a mobile user perspective.
- Check to see if mobile and desktop results are the same.
- Ask for feedback.
Making sure your website is mobile-friendly will boost your SEO rankings in no time.
Step 7. Internal Linking
You’ve seen internal linking before. You have even seen it here at the beginning of an article.

You will see it at the end of this blog post too.

You can see it as a natural part of a text like:

There are internal links at the bottom of this page.

You can see internal links all over the place.
What is the point of it?
Experts from Search Engine Journal put it nicely and comprehensively with a picture.
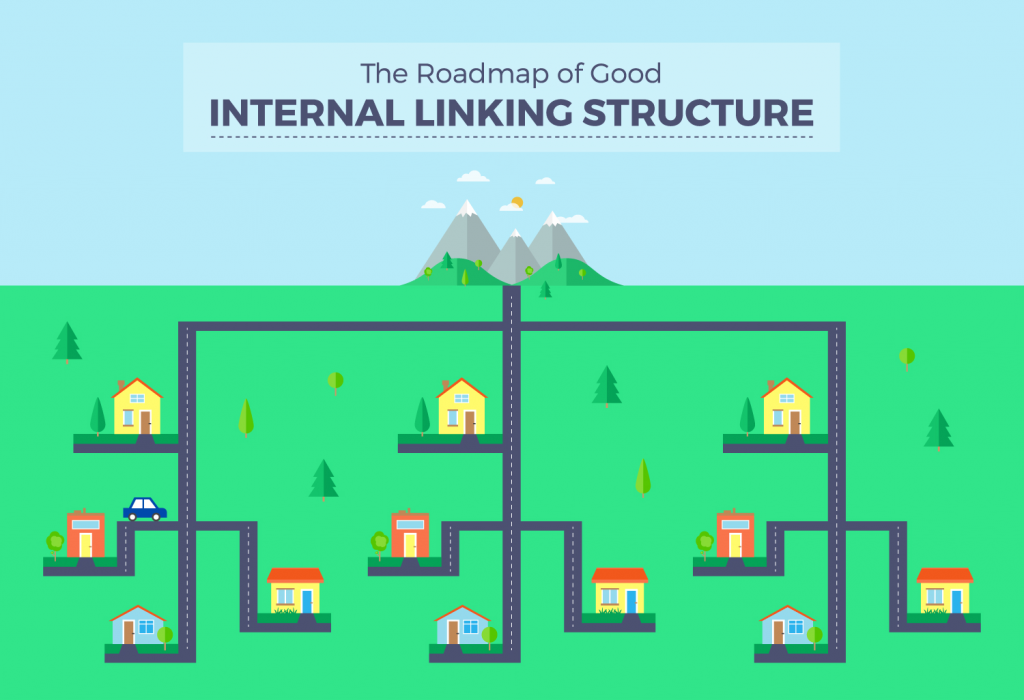
Source: searchenginejournal.com
Your homepage should be accessible from any other page. Category pages should be accessible from the homepage. Relevant blog posts need to link to category pages.
It can look like this.
Here you have a list of the biggest benefits of good internal linking.
✔ It gives a clear picture of the website structure;
✔ Allows users to move around the website;
✔ Creates opportunities to lower the bounce rate (once visitors click such a link);
✔ Keeps the Google Bot within your domain longer;
✔ Shows the hierarchy of content – which pages are more important than others;
✔ Helps spread the link equity;
✔ Increases your site’s dwell time and session duration.
Your internal linking strategy has to be well-designed. You can’t just link one page to another randomly and hope that it works. It is best when internal links are relevant.
It should look more like in the image below.
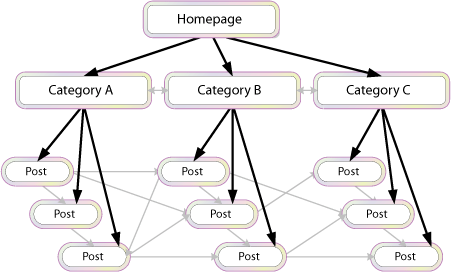
You want to check for any broken links and fix them. Every broken internal link on your website will send the user to a 404 page, resulting in a poor user experience. 404 pages usually come from improperly managing tag pages, archive pages, and deleting pages instead of redirecting them.
It also applies to web crawlers. If you send the web crawler onto a 404 page, it won’t be pleased.
Step 8. Redirections
This topic is tied close to the internal linking chapter.
Lots of people make mistakes here.
First off, don’t delete a web page within your domain!
Creating and publishing a web page makes an URL address as well. It is indexed by Google and kept in their database.
Instead of deleting a web page, you should use a 301 redirection.
You can set up a 301 redirection in a few ways.
- With your Content Management System plugin.
- .htaccess file.
| Zombie Pages: If you already deleted some pages, it’s not the end of the world. You can also redirect all the 404 pages using the same method. |
In the “Tools” section, we mentioned Screaming Frog or DeepCrawl, which will help you find broken links and crawl errors. Some of them will set the 301 redirection automatically.
Step 9. Backlink Profile and Trust Flow
Let’s assume that you have your technical SEO on point and you hired the best copywriters to create your content, yet you receive no traffic.
The reason for that may be a weak link profile.
You have a few options to check your link profile. We’ll give you a few free ones as well as paid ones.
First, Google Search Console.
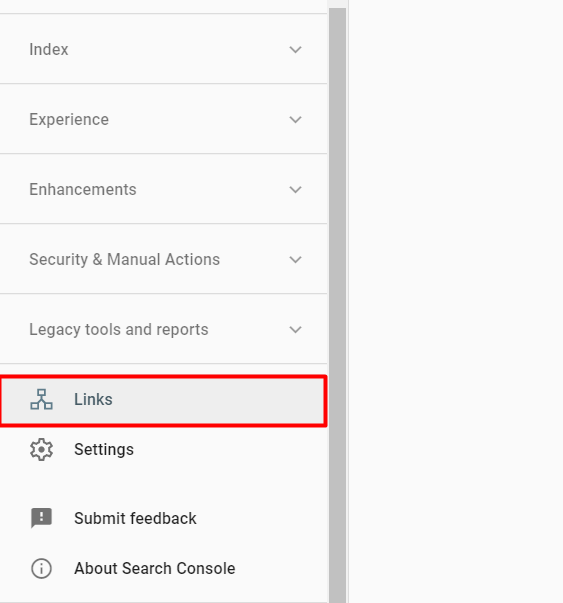
Here, you can see how many links your domain has and from which domains they come.
Then, you can go to the “Tools” chapter and choose one of the backlink checking tools. Your best free options will be UberSuggest and OpenLinkProfiler. For advanced SEO efforts, you should select Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Majestic.
Step 10. Page Load Speed Check
It is said that the ideal page load time should be shorter than 2,5 seconds. After that, there is a high chance that the user will go back to search results.
Page Load time is what influences bounce rates the most.
Read Also: Does Page Speed Affect SEO? Avoid These Mistakes!
What can slow your page down? The most common issues are:
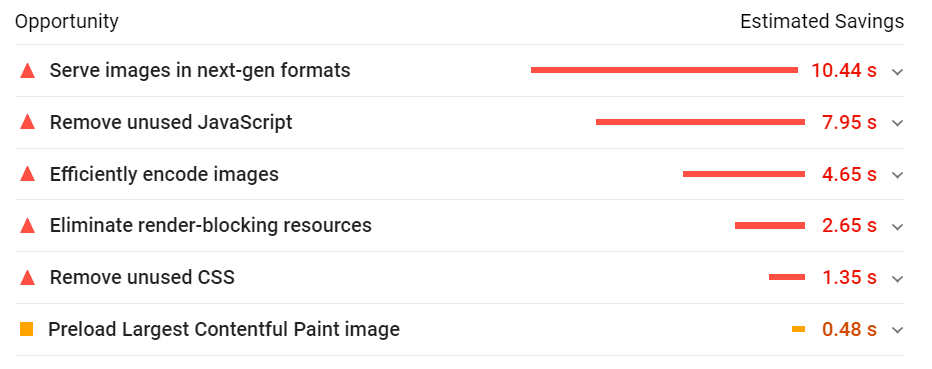
Further diagnostics show more problems.

| Protip: Flashy site elements like carousels, sliders, post grids, animations, etc., look cool, but they need to execute a lot of javascript. Do not use them if you don’t have to. |
We’ve got a list of best practices for your team members:
- Use lazy load.
- Defer off-screen images.
- Optimize images and video files.
- Move scripts to <footer>.
- Preload the most critical resources (like fonts).
- Make above-the-fold content load as fast as possible.
Step 11. Competitor Analysis
You can’t really reinvent the wheel in SEO. Current SEO is all about competition.
The rule is simple. Valuable websites are at the top of the SERP.
You need to follow the leaders to catch up. Once you’re equal to them, you can start thinking about overtaking their position.
There are a few things your competition does that you can follow.
- Keyword selection – There is a lot to it. Let’s break it down:
- Top keywords – These are obviously the ones your rivals own, meaning they’re doing their job well;
- Content gaps – You can find keywords your competitors aren’t ranking for and attack them. You should also nail the keywords they are ranking for, and you’re not, and fill the gap ASAP;
- Topic clusters – These are groups of posts connected topically. You need to cover them up too;
- Keyword opportunities – You’ve got to synchronize your keyword research with competition analysis.
- Common backlinks – If your competitors have a backlink from a certain domain, and you don’t, you’re falling behind.
- PPC campaigns – Wouldn’t it be good to know which keywords are your competitors paying for? Tools like iSpionage or SpyFu give you such an option.
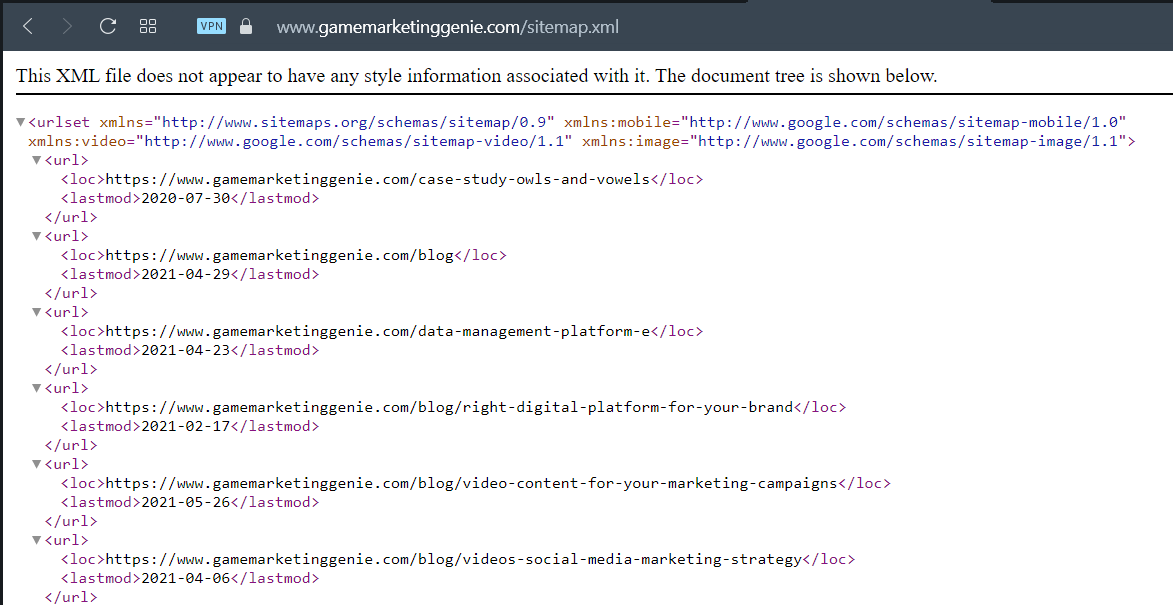
| Protip: You can spy on your competition and see what direction of development they took. Type their domain name in the Google Search Box, and add “/sitemap.xml.” It’ll show you which pages they are currently working on. |
Which SEO Audit Tools are Necessary?
You need to equip yourself with a couple of tools before you begin your SEO audit process. In this chapter, we are listing tools that should be the foundation of your SEO setup, along with some practical tips. Some of these tools are free, and they can be enough for the purpose of a mini audit.
Google Search Console and Google Analytics
Setting it up is not an easy task. If you don’t feel comfortable making changes on the website server or within the code – leave it to an SEO specialist.
Nonetheless, Google Search Console and Google Analytics are necessary for a successful SEO Audit.
Here are the important things from an SEO perspective that you can check in Google Search Console:
- Mobile Friendliness and AMP correctness;
- Core Web Vitals;
- Indexation issues;
- Search queries visibility;
- Organic search performance;
- Site speed errors;
- Structured data errors.
Google Analytics is way more complex, but simple issues can be fixed with Google Search Console.
Complex SEO Site Audit Tools
Some tools allow you to press the button “Audit” and they will do it all.
The essential SEO audit tools are.
| No. | Name | Free Features? | Price (from) |
| 1. | Ahrefs | NO | $99 |
| 2. | SEMrush | NO | $119,95 |
| 3. | Majestic | NO | 46,99€ |
| 4. | MOZ | YES (free trial) | $99 |
| 5. | UberSuggest | YES | $29/month$290/lifetime |
| 6. | SEMstorm | YES | $25/month $250/annually |
| 7. | Senuto | YES (free trial) | 9€/monthly84€/annually |
| 8. | Mangools | YES (free trial) | €49,90€/monthly€358.80/annually |
| 9. | BuzzSumo | YES (free trial) | $99/monthly$948/annually |
Having these tools will basically mean you can perform quite an effective SEO Audit, both on-site and off-site. Make sure to have at least one of them.
Backlink Checker
Here, we are listing tools that are more focused strictly on checking backlinks.
| No. | Name | Free Features? | Price (from) |
| 1. | OpenLinkProfiler | YES | €69,95/monthly |
| 2. | LinkMiner | YES (free trial) | €49,90€/monthly *€358.80/annually |
* you can’t have just LinkMiner, as you need to purchase the whole Mangools package.
Organic Search Traffic Analyzer
Tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or UberSuggest can show your website’s organic traffic. This is just an addition to your Google Analytics reports because no tool is as precise as GA.
However, what it can’t do is analyze your competitors. You will never gain access to your biggest rivals through Google Analytics.
Mobile-Friendly Check
| No. | Name | Free Features? | Price (from) |
| 1. | Google Search Console | YES | 0 |
| 2. | Mobile-Friendly Test | YES | 0 |
| 3. | Test My Site | YES | 0 |
| 4. | Small SEO Tools | YES | 0 |
| 5. | RankWatch | YES | $29 |
| 6. | Merkle | YES | 0 |
| 7. | Web Developer Tools * | YES | 0 |
* To access Web Developer tools, you need to press Ctrl + I in your browser. However, it’s not recommended for beginners.
Broken Link Checker
These site crawl SEO tools will perform a site search and check both internal and external links. With them, you can find and fix your 404 errors.
| No. | Name | Free Features? | Price (from) |
| 1. | Deadlink Checker | YES | $9,95/monthly |
| 2. | Screaming Frog | YES | £149.00 annually |
| 3. | Deep Crawl | YES | (per request) |
| 4. | OnCrawl | YES (free trial) | €49/monthly |
| 5. | Sitebulb | YES (free trial) | £10 + VAT /month |
| 6. | Website Auditor | YES | $124/year |
| 7. | Jet Octopus | YES (free trial) | €25/monthly |
Duplicate Content
Here you have a list of tools to check for duplicate content.
| No. | Name | Free features? | Price |
| 1. | Siteliner | YES (1 free report/30 days) | 1¢/page |
| 2. | CopyScape | YES | 3¢ per search (up to 200 words) plus 1¢ per extra 100 words |
| 3. | Plagiarismcheck.org | YES | $2 |
| 4. | Smallseotools | YES | 0 |
| 5. | Duplichecker | YES | $10/monthly |
| 6. | Grammarly | YES (free account + Chrome extension) | $25/monthly |
| 7. | Plagium | YES | €8/monthly€0,04/page |
Page Speed Test Tools
| No. | Name | Free features? | Price |
| 1. | Page Speed Insights | YES | 0 |
| 2. | GTMetrix | YES | $10/monthly |
| 3. | Key CDN Website Speed Test | YES | $0.04/GB |
| 4. | Lighthouse Report * | YES | 0 |
| 5. | Pingdom Speed Test | YES | $10/monthly |
| 6. | WebPageTest | YES | 0 |
| 7. | Uptrends | YES | $21,59/monthly |
| 8. | Pagelocity | YES | 0 |
* Use Incognito mode to run the test, as extensions and plugins tend to affect the score.
The Conclusion
There you have it – 11 steps to check if your website is fine. With time, you will realize that digital marketing is way more than just SEO. It also touches on the topics of brand awareness, PR, social media platforms presence, and other services. Search in Google for your brand name, and see what pops. It is what people searching for your brand will see.
Is it what you want them to see? Does it match your business goals? Is it visible for your target keyword? If not, now you know how to get started.

A proper strategy will boost your website to host hundreds of thousands of potential clients. At GamerSEO, we can help you with incorporating a proper SEO strategy, including a technical SEO audit. Fill out our contact form and our professionals will reach you ASAP.
We wish you all the best on your way to SEO success.
FAQ
When do I know I need an SEO Audit?
An SEO Audit is like a health check for your site. Whenever you feel like there’s something wrong, you should order one.
Can I do SEO Audit by Myself?
Sure. Simple SEO checks with things like WordPress CMS or GSC with an SEO tool like UberSuggest are accessible even for a newbie. For more technical fixes, you should consider hiring an SEO professional.
How much an SEO audit costs?
It depends on the site’s size, structure, complexity, the total number of URLs, industry, and overall task difficulty. SEO audits prices begin from a couple of hundred dollars for a small blog and go up to dozens of thousands for a huge e-commerce store.
How long does a website audit take?
Depending on the size of your website, an SEO site audit can take from a couple of days to a few weeks.
How often do I need to have an SEO Audit?
Google Bots crawl the whole Internet in 3-6 months. It is also the timeframe for the most impactful changes. For a small company, we suggest performing an audit as the first SEO task and after implementing major changes to the website related to SEO aspects. Audit should be performed on a regular basis for large sites.

SEO enthusiast and digital marketing strategist. My expertise lies in optimizing websites for organic traffic growth and search engine visibility. I carry out, among others, SEO tests, keyword research and analytical activities using Google Analytics. Privately, he is a lover of mountains and bicycle trips.

